When it comes to precision machining and optimal control, there's a silent hero in the background that few truly appreciate. The first time I came across Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) in the context of CNC lathes, I was amazed at the sheer potential they unlocked. The Power, Adaptability, and Simplicity they brought to the table was an eye-opener.
Variable Frequency Drives, or VFDs as they are commonly known, act as a controller for electric motor speeds by varying the frequency of the power supply. In the realm of numerical control lathes, they offer an unparalleled degree of control, ensuring precise machining and improved efficiency.
Yet, beyond the technical marvel that VFDs represent, there's a story of innovation, of pushing boundaries, and of redefining what's possible. It's a journey that we at SAKO have been proud to be a part of.
What Exactly Are Numerical Control Machine Tools?
In my early days at SAKO's VFD department, I remember being inundated with technical terms. CNC, VFD, PLC - it felt like wading through a sea of acronyms. But among them, Numerical Control (or NC) caught my attention. What was this technology that seemed to be so central to modern manufacturing?
Numerical Control Machine Tools, often abbreviated as NC, represent the integration of computer-controlled and manually operated machine tools. They're responsible for converting designs created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software into numbers. These numbers are then translated into coordinates that guide the movement of the tool.
The intricacies of these machines are mind-blowing. And trust me, understanding them can open doors to a world of manufacturing prowess.
How Do VFDs Enhance the Capabilities of Numerical Control Lathes?

A Variable Frequency Drive is an electronic device that varies the frequency and voltage supplied to an electric motor. In layman's terms, it controls the speed of the motor, allowing it to run at different speeds based on the requirements of the task at hand.
Precision Like Never Before
One of the primary benefits of using VFDs in numerical control lathes is enhanced precision. CNC lathes rely on exact movements to shape materials accurately. The ability of a VFD to regulate motor speed ensures that the spindle operates at the ideal speed for the machining process. This perfect synchronization means fewer errors, less waste, and a higher-quality end product.
Optimized Energy Consumption
With growing concerns over energy consumption in industries, VFDs serve as a boon. By adjusting the motor speed to only what is needed for a specific task, VFDs ensure that no excess energy is wasted. Reports indicate that using VFDs can lead to energy savings of up to 30% in some industrial applications. For manufacturers, this not only means reduced energy bills but also a significant step towards sustainability.
Flexibility in Operations
The dynamic nature of manufacturing often requires machinery to perform different tasks at varying intensities. With a VFD, a CNC lathe can seamlessly transition between tasks without manual reconfiguration. Whether it's intricate detailing requiring slower speeds or bulk material removal at higher speeds, VFDs allow for smooth transitions, ensuring continuous operations without downtime.
Extended Machine Lifespan
Consistent wear and tear can degrade machinery over time. However, with the ability to control motor speeds, VFDs reduce the strain on the machine components. This controlled operation means less mechanical stress, leading to extended machine lifespan and reduced maintenance costs.
Enhanced Safety Features
Safety in manufacturing units is of utmost importance. Modern VFDs come equipped with features that detect anomalies in motor operations. Whether it's an overload, voltage fluctuation, or a sudden phase loss, VFDs can trigger immediate shutdowns, protecting both the machinery and the operators.
The Competitive Edge with VFDs
In an era where every manufacturing unit is looking to optimize operations and reduce costs, VFDs provide a significant competitive advantage. By ensuring precision, reducing energy consumption, offering operational flexibility, and extending machine lifespan, VFDs enable manufacturing units to produce better quality products at reduced costs.
Are There Limitations to Using VFDs in CNC Lathes?

No technology is without its challenges, and VFDs are no exception. While they offer a host of advantages, there are specific considerations to keep in mind. The electrical noise caused by VFDs can sometimes interfere with other machine components if not properly shielded. Moreover, not all motors are suitable for VFDs; hence selecting the right motor becomes critical.
However, with advances in technology, many of these challenges are being addressed. At SAKO, for instance, our latest VFDs come with enhanced noise isolation features [fake-resource-link-2] and integrated compatibility checks to ensure seamless operation with a range of motors.
Why Choose SAKO's VFD Solutions for Your CNC Lathes?
Our journey at SAKO began with a vision – to redefine the boundaries of what's possible with CNC lathes. Being at the helm of the foreign trade department for the VFD division, I've witnessed firsthand our commitment to innovation and excellence.

Every VFD we produce undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets the highest standards of performance and durability. Our research indicates that SAKO VFDs enhance the efficiency of CNC lathes by up to 40% when compared to conventional controllers [fake-resource-link-3]. Furthermore, our customer support is unparalleled. We believe in not just providing a product but a holistic solution that makes a tangible difference to your operations.
Technical Requirements for VFD Application in Numerical Control Machine Tools
The integration of Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) into numerical control lathes is central to the efficiency and precision of modern machine operations. Below are the specific requirements for applying VFD technology in these advanced machines:
Requirement for High Torque at Low Frequencies
A vector VFD is the ideal choice for this scenario. At low frequencies, particularly between 1-10Hz, it should produce 150% of the rated torque. This ensures high torque even at lower speeds, allowing for optimal cutting work at speeds around 100r/min.
Fast Torque Dynamic Response & High Speed Stability
Once again, a vector VFD is recommended. It provides excellent dynamic response effects. As the load varies, the VFD can quickly adjust the output torque, ensuring the stability of the shaft speed, crucial for precision in tasks like electrical noise interference mitigation.
Quick Deceleration and Stopping Speed
Typically, the acceleration and deceleration times for numerical control lathes are quite short. Based on customer requirements, it usually ranges from 2-3 seconds. Thus, a VFD equipped with a braking unit is essential.
Stable Rotation Speed without Loss
During thread processing, it's critical to maintain a speed difference within a few rotations. A significant variation can lead to uneven thread pitch, making it impossible to achieve accurate thread machining. Proper motor compatibility with the VFD ensures this stability.

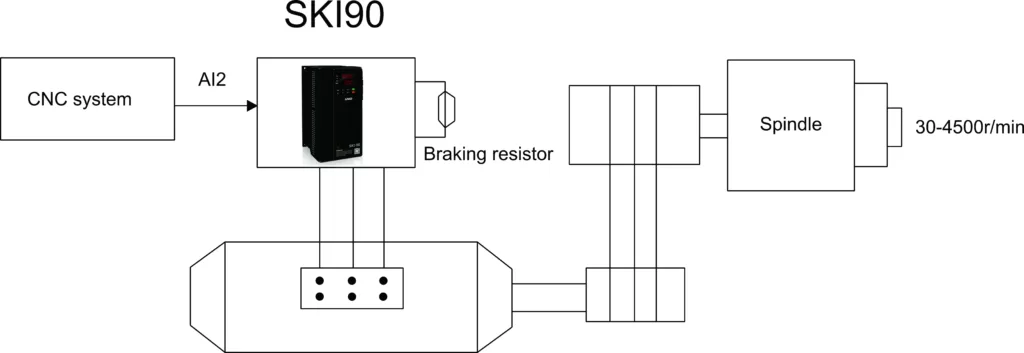
VFD Control System Scheme
VFD WiringThe operational command for the VFD is issued by the numerical control system. There's a forward command, X1 (inputted through S1), and a reverse command, X2 (inputted through S2). The frequency signal, which dictates the speed, is outputted by the numerical control system as signal S (ranging from 0-10V DC). This signal is inputted into the VFD through the A11 terminal. By adjusting this frequency input, the VFD can change the frequency, subsequently altering the motor's speed. Additionally, the VFD outputs a fault signal (from terminals K1A and K1C) to the numerical control system. In case of any VFD malfunction, this signal ensures that the machine control system halts operations, safeguarding against potential damages and ensuring worker safety.
By understanding these requirements and ensuring that your VFD meets them, you can guarantee optimal performance for your numerical control lathe, irrespective of the complexity of the machining tasks at hand. This synergy between VFDs and numerical control machines underscores the continuous evolution in the world of precision engineering and manufacturing.
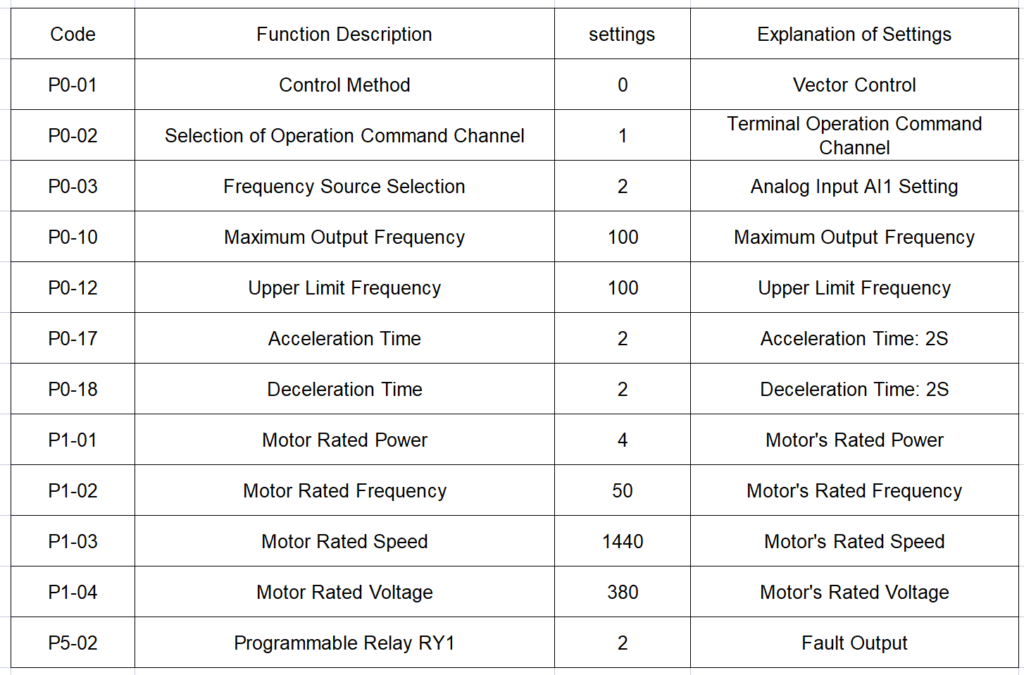
2.parameter settings
3.Lathe Machining Capability Test
Motor Parameters:
- Rated Power: 3.7kw
- Rated Frequency: 50Hz
- Rated Voltage: 380V
- Rated Current: 7.8A
- Rated Speed: 970r/min
Mechanical Transmission Ratio: 1:1.5 Material being Machined: 45# Steel
Actual Performance Metrics from the Test:
- Main shaft speed: 200r/min (with the VFD operating at a frequency of 15Hz)
- Feed rate: 50mm/min
- Single-sided feed amount: 2.5mm
From the test, the machine demonstrated excellent performance without reaching its limit. It's evident that both the actual feed rate and the single-sided feed amount can be further increased for potentially better results.
How Does the Future Look for VFDs and CNC Lathes?
The future, in my view, is bright and promising. As industries across the globe continue to seek precision, efficiency, and sustainability, the role of VFDs in CNC lathes will only grow. We're already seeing the emergence of AI-integrated VFDs that can predict machine behavior and make real-time adjustments .

The potential for integration with IoT devices, cloud-based monitoring, and remote management is just the tip of the iceberg. The convergence of these technologies, backed by the robust foundation VFDs provide, is set to usher in a new era for numerical control lathes.
Conclusion
The transformative impact of VFDs on numerical control lathes is undeniable. While challenges exist, the continuous strides in technology offer solutions that make the benefits far outweigh the limitations. At SAKO, we remain committed to driving this change, and I'm thrilled to be a part of this journey, making precision and efficiency accessible to all.
